Subscribe to get weekly insights
Always stay up to date with our newest articles sent direct to your inbox
Published on 22 Nov, 2024
Updated on 27 Nov, 2024
836 Views
5 min Read

Written by Mudit Handa
favorite0Like
favoriteBe the First to Like
In today’s age of busting life, living a healthy and enriched life seems next to impossible. With high levels of stress and lifestyle-related health problems, people are experiencing their age before it happens. But as the saying goes—
“To lower your body's age you need to stay supple.”
One needs to create an ideal balance between work and life. The disruption of work-life balance has led to several health issues that develop into chronic illnesses. One such serious health condition is oxidative stress.
This article will shed light on the problem of oxidative stress and how to cope with the oxidative stress symptoms to avoid lifestyle diseases.
Oxidative stress refers to a condition of imbalance in the body caused due to excess of free radicals compared to the antioxidants. To understand better, you must first know what antioxidants and free radicals are.
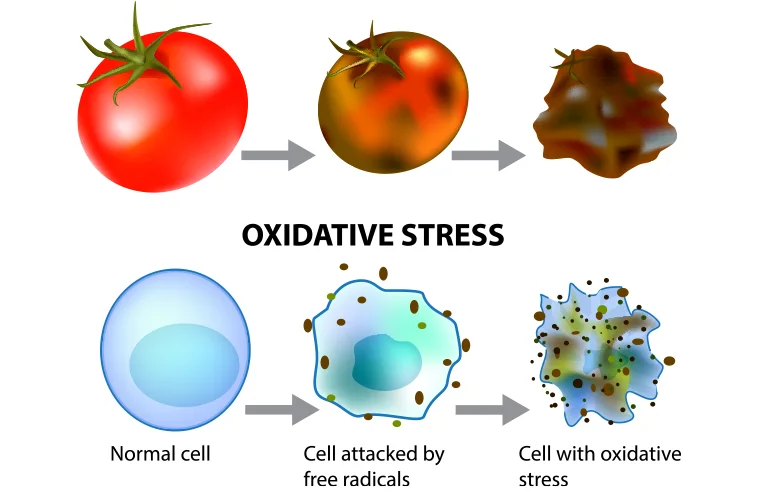
A balance between antioxidants and free radicals is needed to reduce the harmful reaction of free radicals; otherwise, your body cells start decaying quickly. Rapid cell damage due to harmful free radicals is a key factor in many chronic diseases, such as cancer, heart disease, Alzheimer's, premature ageing, and a decrease in lifespan.
The causes of oxidative stress can be internal and external factors. Internal factors may include the following:
External factors of oxidative stress include:
Above mentioned factors gradually increase the harmful effects of free radicals. Additionally, following a sedentary lifestyle accelerates the oxidation process and speeds up cell damage, paving way for more lifestyle related diseases.
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. This imbalance can lead to several negative health effects, including:
Overall, oxidative stress can have a detrimental impact on the human body. By understanding its causes and effects, you can take steps to reduce your risk and protect your health.
No. There is no treatment procedure or medication that can lower your oxidative stress. This is an adverse health condition triggered by lack of nutrition and unhealthy lifestyle. Oxidative stress can be managed by following a healthy lifestyle.
The only way to reduce oxidative stress is to introduce healthy lifestyle changes that include:
>>Read More: Check Out This Miracle Mineral for Stress Relief and Sleep
Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants can reduce oxidative stress. Hence, you must include the following foods in your diet:
However, it’s important to consume eggs, meat, and seafood in moderation. Excess consumption can lead to oxidative stress-related diseases.
These are some healthy lifestyle and dietary habits that can reduce oxidative stress symptoms and prevent chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer.
Apart from reducing oxidative stress, it is equally important to manage mental stress that may occur due to a medical emergency. The best way to do so is—
In today’s time, it's unimaginable to cope with medical costs if a health emergency arises, given the uncontrolled inflation. The only way to stay assured is to have adequate health coverage for major critical diseases such as heart ailments or cancer. Hence, you must buy a suitable health insurance plan for critical illnesses, such as the Care Critical Mediclaim Plan, which guarantees comprehensive coverage of 32 critical illnesses. So, with due concern for your physical and financial health, you should get yourself and your family covered for critical illnesses today itself and live a stress-free life.
Disclaimer: It is essential to verify the policy details and coverage with the official policy documents. Also, kindly consult a professional medical expert to verify the details of health concerns.
favoriteBe the First to Like
Thyroid : मामूली नहीं हैं महिलाओं में थायराइड होना, जानें इसके लक्षण और घरेलू उपचार Vipul Tiwary in Diseases
शुगर कंट्रोल कैसे करे? जानें, डायबिटीज में क्या खाना चाहिए Vipul Tiwary in Health & Wellness
हाई ब्लड प्रेशर को तुरंत कंट्रोल कैसे करें? देखें इसके उपाय Vipul Tiwary in Diseases
पैरों में दर्द किस कमी से होता है? जानें, इसके घरेलू इलाज Vipul Tiwary in Health Insurance Articles
Silent Epidemic: Fatty Liver Disease Now Targeting the Young! Jagriti Chakraborty in Health Insurance Articles
Iodine Rich Foods: The Unsung Heroes of a Healthy Thyroid and a Sharp Mind Jagriti Chakraborty in Diet & Nutrition
Honey, Jaggery & Sugar: Which Sweetener Wins? Jagriti Chakraborty in Health & Wellness
What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Capsicum Every Day? Jagriti Chakraborty in Diet & Nutrition
Always stay up to date with our newest articles sent direct to your inbox
Loading...