Subscribe to get weekly insights
Always stay up to date with our newest articles sent direct to your inbox
Published on 18 Sep, 2024
Updated on 25 Jun, 2025
1786 Views
4 min Read

Written by Mudit Handa
favorite2Likes
We all know that calcium is one of the most integral components of our body and is an essential nutrient for physical growth. Most people believe that the role of calcium in the human body is limited to the formation of bones. Our muscles, too, need a good amount of calcium for mobility and strength. Besides, our nerve cells or neurons require calcium for proper functioning and transmitting messages from our brains to every body organ. Most importantly, calcium plays an integral role in our circulatory system, empowering the blood vessels to flow blood throughout the body and release and carry hormones that support various body functions.
But here is the catch!
Did you know that excessive calcium in the blood can hamper the proper functioning of various organs? This abnormal condition is known as Hypercalcemia. If you are unaware of this fact, this article will help you understand how high calcium affects the heart. Continue reading!
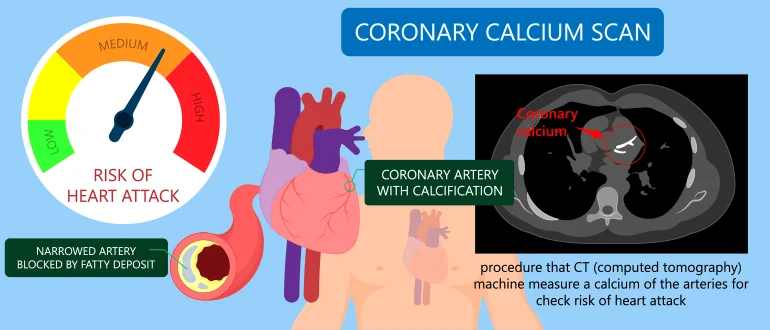
Hypercalcemia is when an excess amount of calcium is present in the blood. This condition can affect the heart's electrical activity, i.e. the electrical impulses that run through the heart's conduction system and cause the heartbeat.
The critical factor causing hypercalcemia is hyperparathyroidism. This is a kind of thyroid malfunction wherein the parathyroid glands become overactive and release excess parathyroid hormone.
The effects of high calcium levels do not always impact the heart functioning. However, in rare cases, high calcium levels in the blood or hypercalcemia may cause serious heart ailments. These may include:
Listed below are several factors responsible for developing hypercalcemia:
How much calcium per day is needed for a healthy body?
According to the World Health Organization, 400 to 500 mg of calcium daily is needed to prevent osteoporosis. In the Indian context, the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) recommends the ideal limit for daily calcium intake for Indians-
Let us now understand a few practical ways to tackle the problem of hypercalcemia.
>> Also Read: What is the Role of Calcium in Our Body?
Specific changes in lifestyle, especially in your diet can help you maintain the optimal calcium level in the heart. These include:
No Smoking, Please! Smoking may result in certain lung diseases, such as Sarcoidosis, that cause hypercalcemia. Moreover, tobacco intake can cause blood cancer, which is another factor behind hypercalcemia.
These are a few ways to prevent high calcium levels in the heart. Both calcium deficiency or excessive calcium level can lead to serious health complications. And despite every precaution taken, you can’t avoid a medical emergency to happen; you can only be prepared for it with a health insurance plan catering to heart-related illnesses.
Besides safeguarding your health against lifestyle diseases, you must plan your finances smartly to protect your savings from going into hospital bills. You can consider our heart mediclaim that offers comprehensive coverage up to 2 crore, covering 16 common heart conditions. For detailed information you can connect with our experts or visit the website.
Disclaimer: Plan features, benefits, coverage, and claims underwriting are subject to policy terms and conditions. Kindly refer to the brochure, sales prospectus, and policy documents carefully.
शुगर कंट्रोल कैसे करे? जानें, डायबिटीज में क्या खाना चाहिए Vipul Tiwary in Health & Wellness
Thyroid : मामूली नहीं हैं महिलाओं में थायराइड होना, जानें इसके लक्षण और घरेलू उपचार Vipul Tiwary in Diseases
हाई ब्लड प्रेशर को तुरंत कंट्रोल कैसे करें? देखें इसके उपाय Vipul Tiwary in Diseases
प्लेटलेट्स की कमी के लक्षण, कारण और इलाज क्या है Vipul Tiwary in Diseases
Struggling to Move Your Shoulder? Try These 7 Frozen Shoulder Treatments Gungun Bhatia in Diseases
Top 10 Surprising Benefits of Pineapple You Shouldn’t Miss Gungun Bhatia in Health & Wellness
Jeera Water for Weight Loss: Simple Drink With Healthy Benefits! Sejal Singhania in Health & Wellness
8 Untold Benefits of Vitamin D in Baby Development Jagriti Chakraborty in Diet & Nutrition