Subscribe to get weekly insights
Always stay up to date with our newest articles sent direct to your inbox
Published on 14 Jan, 2025
Updated on 11 Apr, 2025
3206 Views
5 min Read

Written by Anjali Sharma
Reviewed by Rashmi Rai
favorite2Likes
The urinary bladder is an important organ in our body’s excretory system. It temporarily stores urine and plays a significant role in maintaining our overall health. The bladder works in coordination with the kidneys, ureters, and urethra to form the urinary tract, ensuring the proper removal of waste products and maintaining the body's fluid balance.
In this blog, we will explore the urinary bladder, its functions, its location, and some common medical conditions related to it.
The urinary bladder is a hollow, muscular organ in the urinary tract. It stores urine produced by the kidneys and helps control its release during urination. The urinary bladder has elastic walls that can expand to hold urine and contract to expel it. On average, a healthy urinary bladder has the capacity to hold about 500 mL of urine, although you might feel the urge to urinate when it holds around 200–300 mL. The shape of the urinary bladder depends on the amount of urine stored in it.
Here is a detailed explanation of the main functions of the urinary bladder:
Storing Urine: The primary function of the urinary bladder is to store the urine made by the kidneys. The two small tubes present, called ureters, carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
Emptying: When the bladder becomes full, it sends signals through the nerves to the brain. Then, the bladder wall contracts and flattens to expel the urine through the urethra.
The urinary bladder is a key part of the urinary system, located within the pelvic cavity. Its specific position and relationships with surrounding organs differ based on gender. In males, it is located above the prostate gland and in front of the rectum. However, in females, it is located below the uterus and in front of the vagina. This location of the Urinary bladder ensures efficient connection with the kidneys, ureters, and urethra for optimal urinary function.
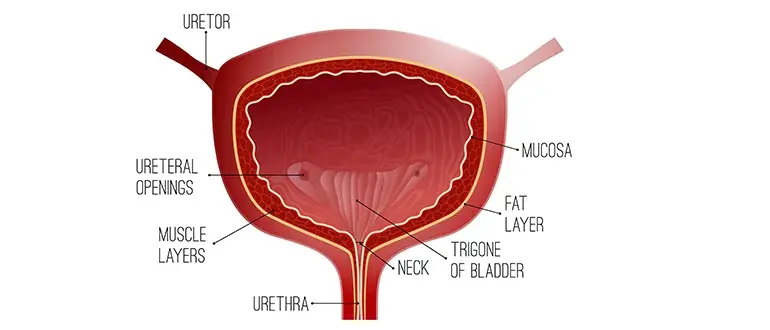
The urinary bladder is a balloon-like organ that can stretch when it is filled with urine and shrink when empty. Let us learn in detail about the anatomy of the urinary bladder:
The urinary bladder is a muscular organ in your lower belly that holds urine until you go to the bathroom. It is stretchy and can expand or shrink depending on how much urine it holds.
It is well-structured and has several parts in it. Let us learn more about the structure of the urinary bladder in detail:
Shape and Size: When the urinary bladder is empty, it looks like a small, deflated balloon. When it becomes full, it becomes larger. In adults, a urinary bladder can hold 400–600 mL of urine (about two cups).
Openings in the Bladder: There are two small tubes, known as ureters that bring urine from the kidneys to the bladder. A single tube known as urethra is also present that takes urine from the bladder out of the body during urination.
Nerves and Blood Supply: The nerves in the urinary bladder wall send signals to your brain to let you know when it is time to urinate. They also control the muscles that help release or hold urine. The arteries also play a vital role by bringing oxygen-rich blood to the bladder, and the veins carry blood back to the heart after oxygen is used.
The urinary bladder is an elastic muscular organ prone to various medical conditions that can affect its functionality.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Bacterial infections that enter through the urethra and reach the bladder cause urinary tract infections. Consuming antibiotics and increasing the daily fluid intake would help in reducing the symptoms.
Overactive Bladder (OAB): It is a medical condition in which the bladder creates an urgency and incontinence to excrete urine. Some lifestyle changes, pelvic floor exercises, and medications are very helpful to manage the situation of overactive bladder (OAB).
Bladder Stones: The stones in the urinary bladder are the hard mineral deposits that form due to incomplete bladder emptying. Multiple or large stones in the bladder can cause chronic urinary retention or infection.
Bladder Cancer: It is a form of cancer that causes cells in the urinary bladder to grow uncontrollably. It usually starts in the cells of your urothelium. Multiple treatment methods, such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, or immunotherapy, are useful in the curing of urinary bladder cancer.
Understanding the anatomy and common medical conditions of the urinary bladder can empower you to take proactive steps to maintain urinary bladder health and seek timely medical attention when necessary.
Here are some simple tips to maintain a healthy bladder:
The urinary bladder is a vital organ with the essential role of storing and releasing urine, ensuring the smooth functioning of the body’s excretory system. Maintaining a healthy bladder through good hydration, regular hygiene, and lifestyle habits is essential.
Treating bladder-related conditions can sometimes lead to unexpected medical expenses. This is where health insurance becomes a critical safety net. A comprehensive health insurance policy can cover diagnostic tests, treatments, medications, and even surgeries related to bladder health, ensuring you receive timely and quality care without financial stress.
>> Also Read: 5 Warning Signs of Bladder Infection
Disclaimer: Verifying the policy details and coverage with the official policy documents is essential. Also, kindly consult a professional medical expert to verify the details of health concerns.
Thyroid : मामूली नहीं हैं महिलाओं में थायराइड होना, जानें इसके लक्षण और घरेलू उपचार Vipul Tiwary in Diseases
शुगर कंट्रोल कैसे करे? जानें, डायबिटीज में क्या खाना चाहिए Vipul Tiwary in Health & Wellness
हाई ब्लड प्रेशर को तुरंत कंट्रोल कैसे करें? देखें इसके उपाय Vipul Tiwary in Diseases
पैरों में दर्द किस कमी से होता है? जानें, इसके घरेलू इलाज Vipul Tiwary in Health Insurance Articles
Cold Hands? Act Immediately Against Raynaud’s Phenomenon Jagriti Chakraborty in Diseases
Understanding Azotemia: Meaning, Causes, Treatment & ICD 10 Guide Leena Khowal in Diseases
Leukaemia vs. Lymphoma Breakdown: What Sets Them Apart Leena Khowal in Diseases
When Silent Clots Threaten Your Life: DVT Pratham Gupta in Diseases
The hernia of the urinary bladder occurs when part of the bladder protrudes into an abnormal position, often through a weakened area in the abdominal or pelvic wall.
There are some common signs and symptoms of urinary bladder problems, such as the inability to hold urine, cloudy urine or blood in the urine. Also, a burning sensation or pain before, during, or after urinating might also be experienced.
Always stay up to date with our newest articles sent direct to your inbox
Loading...