Subscribe to get weekly insights
Always stay up to date with our newest articles sent direct to your inbox
Published on 6 Sep, 2023
Updated on 23 Sep, 2025
1533 Views
6 min Read

Written by Sejal Singhania
Reviewed by Munmi Sharma
favorite0Like
favoriteBe the First to Like
Signs of a Brain Tumour, Causes, Treatment and More!
We all experience headaches from time to time, whether it's due to stress, lack of sleep, or simply staring at your phone or laptop for too long. However, if you notice that a headache persists or is accompanied by blurred vision, nausea, or sudden memory loss, it's essential to pay attention. Most headaches are harmless, but occasionally, they can be a sign of something more serious, like a brain tumour.
A brain tumour is a growth of abnormal cells in the brain, which can be either cancerous or non-cancerous. While it is a serious condition, understanding it can make a significant difference. Early detection improves treatment options and recovery prospects. Let's explain in simple terms what it is, the early signs of a brain tumour and explore how modern medicine combats it.
A brain tumour is a growth of cells in or near the brain. These tumours can develop within the brain tissue itself or in nearby areas. Such locations include nerves, the pituitary gland, the pineal gland, and the membranes that cover the brain's surface.
Brain tumours can be cancerous or benign, like other tumours in the body. Since the skull encloses your brain, pressure from a tumour can cause tension in the skull and other issues. A diagnosis is needed to determine severity. Tumours vary in size; small ones may cause symptoms if they occur in active brain areas, but those in less-active parts might not cause immediate symptoms.
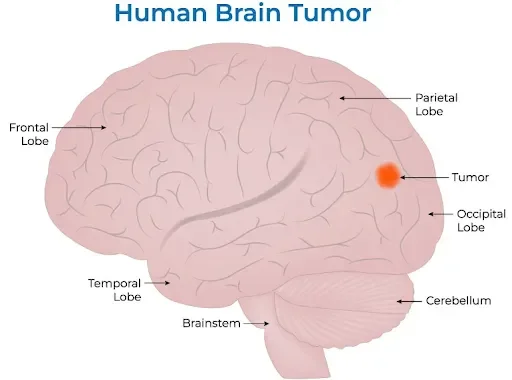
Brain tumours are classified based on their original location and the severity they pose to the person. The following are the types of brain cancer you should know about:
As the name suggests, a primary brain tumour develops in the brain itself. It may grow at various locations in the brain. A primary brain tumour can grow in:
Any tumour that reaches the brain from any other body part, like the breast, lungs, kidney, etc., is known as a secondary tumour. It is also known as a metastatic tumour. Metastasised brain tumours may spread from:
Tumours can be cancerous or non-cancerous. Since the brain is extremely sensitive and surrounded by the skull, even non-cancerous tumours can cause various complications.
Cancerous brain tumours are known as malignant brain tumours. They grow rapidly and can also spread to other parts of the brain. Such tumours may turn life-threatening.
All non-cancerous brain tumours are known as benign tumours. Typically, two-thirds of brain tumours are benign. They have slow growth, and surgeries can be more effective for benign tumours.
Depending on the location and size of the brain tumour, its symptoms may vary. Some of the common signs of a brain tumour are:
In the case of pituitary brain tumours, you may experience the following brain cancer symptoms:
Usually, how brain tumours occur can’t be known. Specific chromosome genes get damaged and can’t function anymore. The doctor believes this happens when genetic mutations cause brain cells to multiply uncontrollably. Possible risk factors for brain tumour include:
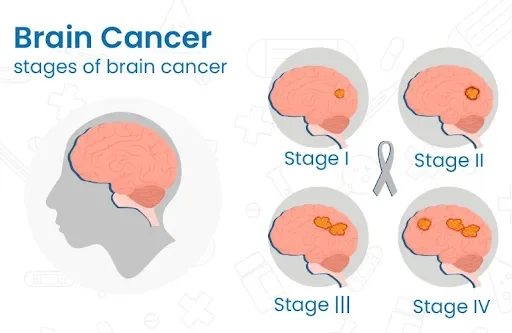
Brain tumours are classified on a scale from I to IV, where higher grades denote more aggressive and malignant growths. Unlike other cancers, such as those in the lung, colon, or breast, which are staged based on their location, size, lymph node involvement, and spread, brain cancer grading focuses on how aggressive the tumour cells look under a microscope. Brain tumours are categorised into four grades:
If you notice any unusual changes in your body, it’s very important to pay attention, especially if symptoms appear suddenly or worsen over time. Don’t hesitate to talk to your doctor about any symptoms you experience, as they might indicate other health concerns. See a doctor if you encounter any of these symptoms:
The doctor conducts a neurological exam, including symptoms, health history, treatments, and lifestyle, to diagnose the disease properly. Any of the following scans can be used to diagnose tumours:
Several factors decide the treatment of brain tumours, such as:
The following are the brain tumour treatment options:
Although we can't prevent every brain tumour, embracing a healthy lifestyle helps reduce the risk and keep our brains healthy overall. Some common tips to avoid brain tumours include:
Cancer is often a silent disease, and hearing about a brain tumour can be quite stressful. But don't worry—getting thorough examinations and tests can lead to a proper diagnosis. Whether a tumour is malignant or benign, it can cause various challenges for your brain and overall health. To help you feel more secure financially, consider investing in our Cancer Insurance Policy. It includes 32 different critical illnesses, including benign tumours. With coverage of up to 2 crores, you can plan your treatment expenses comfortably, without worrying about financial strain.
>>Also Read: What is Carcinoma? Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Brain tumours can significantly impact your life, so it's a good idea to stay proactive about your health. If you're at risk, regular check-ups can make a big difference. Remember, routine medical visits are beneficial for everyone. Thinking about a critical illness plan can also be a smart move to help manage rising treatment costs. Protecting yourself and your savings with health insurance shows you care about your well-being and that of your loved ones.
Disclaimers: The above information is for reference purposes only: Policy Assurance and Claims at the underwriter's discretion. All plan features, benefits, coverage, and claims underwriting are subject to policy terms and conditions. Kindly refer to the brochure, sales prospectus, and policy documents carefully.
favoriteBe the First to Like
Thyroid : मामूली नहीं हैं महिलाओं में थायराइड होना, जानें इसके लक्षण और घरेलू उपचार Vipul Tiwary in Diseases
शुगर कंट्रोल कैसे करे? जानें, डायबिटीज में क्या खाना चाहिए Vipul Tiwary in Health & Wellness
हाई ब्लड प्रेशर को तुरंत कंट्रोल कैसे करें? देखें इसके उपाय Vipul Tiwary in Diseases
पैरों में दर्द किस कमी से होता है? जानें, इसके घरेलू इलाज Vipul Tiwary in Health Insurance Articles
Cold Hands? Act Immediately Against Raynaud’s Phenomenon Jagriti Chakraborty in Diseases
Understanding Azotemia: Meaning, Causes, Treatment & ICD 10 Guide Leena Khowal in Diseases
Leukaemia vs. Lymphoma Breakdown: What Sets Them Apart Leena Khowal in Diseases
When Silent Clots Threaten Your Life: DVT Pratham Gupta in Diseases
Survival rates for brain tumours differ greatly depending on the tumour type and grade. Low-grade tumours have a survival rate of over 90%, while malignant tumours such as glioblastoma have a 5-10% five-year survival rate.
Yes, a brain tumour can substantially influence behaviour, leading to personality changes, mood swings, heightened aggression, disinhibition, apathy, or depression.
Yes, full recovery from a brain tumour is possible, especially if it's non-malignant, entirely removed, and diagnosed early. However, the outcome depends on the tumour's type, grade, size, location, and the person's overall health and treatment response.
The most common brain tumours in young adults (15-39) are gliomas, followed by pituitary and nerve sheath tumours. Although gliomas are the most common overall, pituitary adenomas are the most frequent in the younger AYA group.
Brain tumour growth rates vary significantly depending on the tumour type. Benign tumours grow slowly, taking months or years to show symptoms. Malignant tumours, like glioblastoma, grow faster, sometimes doubling in size in weeks.
Always stay up to date with our newest articles sent direct to your inbox
Loading...